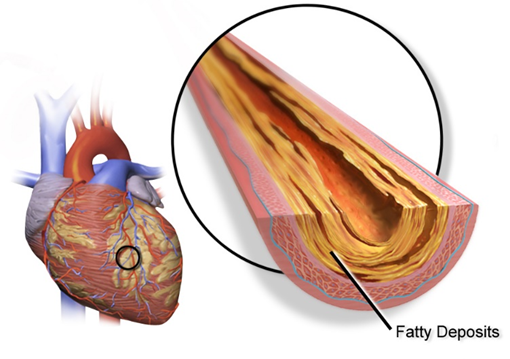
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a common cardiovascular condition that affects millions of people worldwide. As a heart surgeon, it’s essential to educate yourself about CAD and, more importantly, for patients to understand this condition better. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for coronary artery disease.
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease:
CAD occurs when the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle become narrow or blocked. This happens due to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis. Several factors contribute to the development of CAD:
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, a high-fat diet, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption can all contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in CAD. If your parents or close relatives have had heart disease, your risk may be higher.
- Age: As we age, the risk of CAD increases.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels can accelerate the progression of CAD.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease:
The symptoms of CAD can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all until a significant blockage occurs. Common symptoms include:
- Chest Pain (Angina): This is the most typical symptom. It can feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the chest, often triggered by physical exertion or stress.
- Shortness of Breath: As the heart’s blood supply becomes restricted, you may experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Fatigue: Reduced blood flow to the heart can lead to fatigue and a feeling of weakness.
- Heart Attack: In severe cases, a sudden, intense chest pain may indicate a heart attack, which requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment Options for Coronary Artery Disease:
Managing CAD involves various approaches, depending on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors. As a heart surgeon, I often recommend:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial. This includes quitting smoking, eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress.
- Medications: Medications like statins, aspirin, beta-blockers, and nitroglycerin can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: In cases where the blockage is severe, a procedure called angioplasty, followed by stent placement, can be performed to open the narrowed arteries.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): For complex cases or multiple blockages, CABG surgery may be necessary. This involves using blood vessels from elsewhere in the body to bypass the blocked coronary arteries.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: After any procedure or surgery, cardiac rehabilitation is crucial to help patients recover and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
In conclusion, coronary artery disease is a prevalent condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. Recognizing its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. If you or a loved one is experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the outlook for individuals with CAD.
