Author: Dr. Bhasker Semitha, Consultant Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgeon
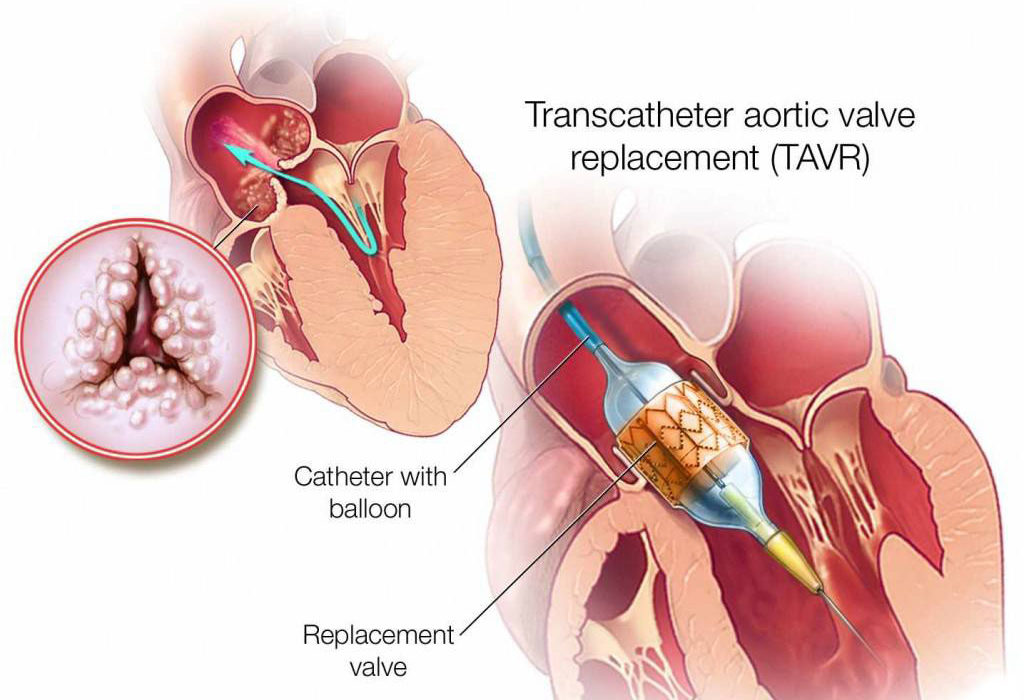
Understanding Heart Valve Disorders
Before diving into the specifics of heart valve surgery, it’s important to understand the types of heart valve disorders and their implications. Heart valve disorders are categorized into two main types:
- Stenosis: Valve stenosis occurs when a valve becomes narrowed or constricted, restricting blood flow through the valve. This condition forces the heart to work harder to push blood through the narrowed opening.
- Regurgitation (Insufficiency or Incompetence): Valve regurgitation happens when a valve doesn’t close properly, allowing blood to flow backward into the chamber it just left. This can lead to an inefficient circulation and can strain the heart.
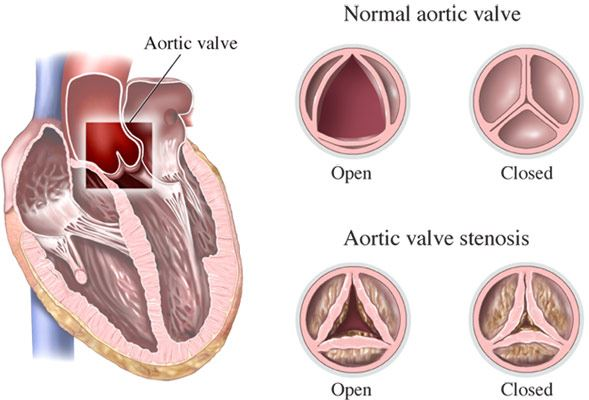
Indications for Heart Valve Surgery
Heart valve surgery is recommended when the severity of a valve disorder jeopardizes a patient’s overall health and quality of life. Indications for heart valve surgery may include:
- Severe Symptoms: Patients with symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, or fainting due to a heart valve disorder may require surgery.
- Worsening Condition: If the valve disorder progressively worsens, it can lead to heart failure, which is a life-threatening condition that often necessitates surgery.
- Reduced Heart Function: When the heart’s ability to pump blood is compromised due to valve disease, surgery may be needed to improve function.
- Valve Infection: Infections of heart valves, known as infective endocarditis, often require surgical intervention to remove infected tissue and repair or replace the valve.
Types of Heart Valve Surgery
There are two primary types of heart valve surgery, each with its own approach and considerations:
- Valve Repair: In valve repair surgery, the surgeon preserves the patient’s own valve tissue and repairs the damaged or faulty valve. This approach is preferred when possible, as it can provide a more natural and durable solution.
- Valve Replacement: When a valve is severely damaged and cannot be repaired, a valve replacement is necessary. This involves replacing the damaged valve with either a mechanical valve (made from artificial materials) or a biological valve (often harvested from animals or donated human tissue).
Outcomes of Heart Valve Surgery
The outcomes of heart valve surgery have improved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in surgical techniques, technology, and post-operative care. Patients can generally expect the following outcomes:
- Symptom Relief: Heart valve surgery aims to alleviate symptoms and improve a patient’s quality of life. Many patients experience reduced chest pain, improved breathing, and increased energy levels after surgery.
- Prolonged Life: Surgery can extend the lifespan of individuals with severe valve disorders, especially those at risk of heart failure.
- Enhanced Heart Function: Restoring proper valve function can help the heart pump blood more efficiently, reducing strain on the heart muscle.
- Rehabilitation: Patients typically undergo cardiac rehabilitation programs to aid in their recovery, regain strength, and learn to manage their heart health.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with a cardiologist are crucial to monitor the performance of the repaired or replaced valve and to address any potential issues.
Conclusion
Heart valve surgery is a life-saving procedure for individuals with severe valve disorders. With advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, the outcomes of these procedures have significantly improved, offering patients relief from debilitating symptoms, an extended lifespan, and improved heart function. If you or a loved one is facing the possibility of heart valve surgery, it’s essential to consult with a cardiovascular specialist to determine the most suitable approach and discuss expectations for a successful outcome.
